Investigating the biblical and archaeological evidence for the Philistines’ origins
Megan Sauter March 23, 2022 0 Comments 386 views


Philistine Pottery. These pottery pieces from Ashkelon bear early Philistine decorations. Photo: © The Leon Levy Expedition to Ashkelon.
The Philistines are best known from the Bible as the Israelites’ enemies, but they were much more than that. Recent archaeological discoveries help inform our understanding of their culture, economy, and even origins. In the Spring 2022 issue of Biblical Archaeology Review, Daniel M. Master of Wheaton College looks at the biblical and archaeological evidence for the Philistines’ roots in “Piece by Piece: Exploring the Origins of the Philistines.”
Who Were the Philistines?
In the Bible, the Philistines are remembered as an uncircumcised people with advanced technology and a formidable military (Judges 14:3; 1 Samuel 13:19–20; Exodus 13:17). The Philistines frequently encroached on Israelite territory, which led to some battles, including the famous clash between David, the Israelite, and Goliath, the Philistine (1 Samuel 17). They were condemned for being idol worshipers (1 Samuel 5:1–5) and soothsayers (Isaiah 2:6). In short, the Philistines are portrayed quite negatively in the Bible.
They lived in the cities of Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, Gath, and Gaza—the heartland of ancient Philistia on the Mediterranean Sea’s southeastern shore. Ashdod, Ashkelon, Ekron, and Gath have been excavated in recent decades. The findings from these cities show that the Philistines had distinct pottery, weapons, tools, and houses. They also ate pork and had vast trade networks.
Philistine culture flourished during the Iron Age (12th through sixth centuries B.C.E.). Similar to the kingdoms of Israel and Judah, the Philistines lost their autonomy toward the end of the Iron Age. They became subservient and paid tribute to the Assyrians, Egyptians, and then Babylonians, the great superpowers of the region who severely punished rebellion. For example, the Babylonian king Nebuchadnezzar destroyed disloyal Ashkelon and Ekron and carried off many Philistines into exile.
Where Did the Philistines Come From?


Philistine Portrait? A confederation of island tribes, including the Peleset (Philistines), attacked Egypt in the 12th century B.C.E. This relief from Medinet Habu records a sea battle between the two forces. Photo: Olaf Tausch, CC BY 3.0, via Wikimedia Commons
In his article, Daniel Master looks at archaeological and biblical evidence for the Philistines’ origins. He considers the accounts at Ramesses III’s mortuary temple at Medinet Habu. In the 12th century B.C.E., during the reign of Ramesses III, a confederation of tribes from the “islands” of the “northern countries” attacked Egypt—several times, both on sea and land. The Peleset, whom scholars connect with the Philistines, was named as one of these tribes. On the way to Egypt, the confederation had traveled through the eastern Mediterranean and destroyed numerous cities, including Ugarit on the Syrian coast. Ammurapi, the last king of Ugarit, had written to surrounding kingdoms for help, when the “seven ships of the enemy” had arrived to ransack his kingdom. By the time help had come, though, it was too late: Ugarit lay in ruins.


Battle Ships. This drawing of a relief at Medinet Habu shows a sea battle between the Egyptians and people from the “islands,” who had invaded Egypt in the 12th century B.C.E. Photo: Public Domain.
Egypt defeated the confederation, as recorded on one of the temple walls at Medinet Habu. A relief from that temple also depicts a sea battle between the island tribes and the Egyptians. In it, the islanders wear distinct headdresses, which clearly set them apart from the Egyptians. After being defeated, some of these tribes settled on the southern coast of Canaan—in what would become the land of the Philistines. Egyptian sources, thus, seem to record a migration of people from the “islands” to Philistia.
Master also examines the evidence for Philistine origins in the Bible. The biblical authors remembered the Philistines as coming from a foreign land, from “Caphtor” (Genesis 10:14; Deuteronomy 2:23; 1 Chronicles 1:12; Amos 9:7; Jeremiah 47:4). Scholars have long drawn a connection between Caphtor and Crete. This is largely based on Egyptian inscriptions and paintings of “Keftiu” from the 15th and 14th centuries B.C.E., wherein the Keftiu are linked to the Minoan civilization, which was centered on Crete.
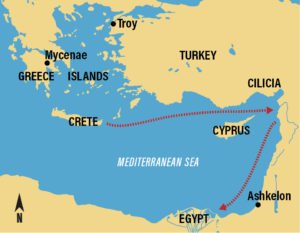

Migration Map. Who were the Philistines, and where did they come from? New archaeological evidence suggests that many of the Philistines originally came from Crete, called “Caphtor” in the Bible. Map: © Biblical Archaeology Society.
Excavations have shown that the Philistines had a distinct assemblage of artifacts. Master notes parallels between some early Philistine objects, especially from the 12th and 11th centuries B.C.E., and Aegean and Cypriot artifacts. Elements of Philistine material culture, then, also hint at an Aegean or Mediterranean origin for the Philistines.
New evidence from Ashkelon further supports this connection. The Leon Levy Expedition excavated at Ashkelon from 1985–2016 under the direction of the late Lawrence Stager at Harvard University; for the last decade, Daniel Master co-directed excavations. They found some infant burials from the 12th century B.C.E., as well as a Philistine cemetery with burials from the 11th through eighth centuries B.C.E. Teaming up with scientists at the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, they were able to analyze DNA from seven of these individuals. When they looked at the 12th-century infants’ DNA, they discovered that the infants had some European ancestry. Crete proved to be one of the best matches for the infants’ heritage—when considering all of their genetic material. Yet other places in the western Mediterranean, such as Iberia, also provided a good match.
Interestingly, in the later individuals from Ashkelon’s cemetery, this European ancestry had been so diluted to barely register. Master explains that, by the tenth century B.C.E., enough intermarriage had taken place between the Philistines and the local Levantine population that the Philistines looked a lot like their neighbors:
While there was some evidence of the same Western European Hunter-Gatherer genetic input, for all statistical purposes, it could not be identified for certain. The best models showed that these people [the tenth- and ninth-century individuals buried in Ashkelon’s cemetery] were descendants of both the 12th-century inhabitants and the earlier Bronze Age inhabitants. It appears from these results that so much intermarriage had taken place between the original immigrants and the people around them that the genetic makeup of Ashkelon’s inhabitants had lost its immigrant distinctiveness.
Yet Master clarifies that, at this point in history, the Philistines still thought of themselves as distinct, as evident in a seventh-century inscription from the Philistine city of Ekron. The inscription names Ekron’s king as Ikausu, which means “Achaean” or “Greek.” The name Ikausu (or Achish) also appears in 1 Samuel 21:10 as Gath’s king.
The Philistines remembered their foreign origins.
Master concludes that the new DNA evidence, coupled with the biblical and archaeological testimonies, suggests that the Philistines originated in Crete. That is not to say that the Philistines were a homogenous group, all coming from the Aegean world, but it seems that many Philistines did indeed migrate from there, bringing with them vestiges of Minoan culture. Learn more about this ancient people in Daniel M. Master’s article “Piece by Piece: Exploring the Origins of the Philistines,” published in the Spring 2022 issue of Biblical Archaeology Review.
——————Subscribers: Read the full article “Piece by Piece: Exploring the Origins of the Philistines” by Daniel M. Master in the Spring 2022 issue of Biblical Archaeology Review.

