Understanding the Cenacle on Mount Zion
Jesus sent Peter and John, saying, “Go and make preparations for us to eat the Passover. […] As you enter the city, a man carrying a jar of water will meet you. […] He will show you a large room upstairs, all furnished. Make preparations there.” (Luke 22:7–12)
This two-story stone building atop Mount Zion (below) ranks among the most intriguing sites in Jerusalem. It is traditionally called the Cenacle (from the Latin coenaculum, “dining-room”) and you will find it just outside the present-day Old City walls to the south (see map). The building’s lower story has been associated since the Middle Ages with the Tomb of David, the purported burial place of the Biblical King David, while the upper story—often referred to in English as the “Upper Room”—is traditionally believed to be the place of Jesus’ Last Supper.1
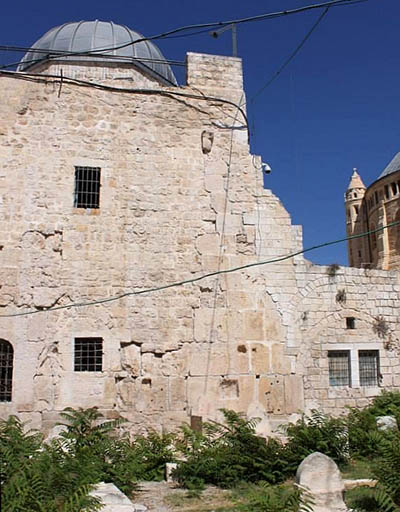


Masonry of the Cenacle’s eastern wall clearly demonstrates its “layered” history—from the Second Temple period through the Byzantine and Crusader periods to the Ottoman period. Visible on the right is the Dormition Abbey. Photo: Courtesy of David C. Clausen.
Even though it suffered numerous natural and man-inflicted disasters and was claimed and successively held by the faithful of all three monotheistic religions, the Last Supper Cenacle remains standing as a testimony to a long-shared sacrality in the Eternal City. It has been a church, a mosque and a synagogue.
It was not until quite recently, however, that the location of Jesus’ Last Supper and the identity of this particular building were questioned and became an object of scholarly debate. David Christian Clausen, adjunct lecturer in Religious Studies at the University of North Carolina at Charlotte, examines the evidence for various claims regarding the historical purpose of the Cenacle in his Archaeological Views column “Mount Zion’s Upper Room and Tomb of David” in the January/February 2017 issue of Biblical Archaeology Review.
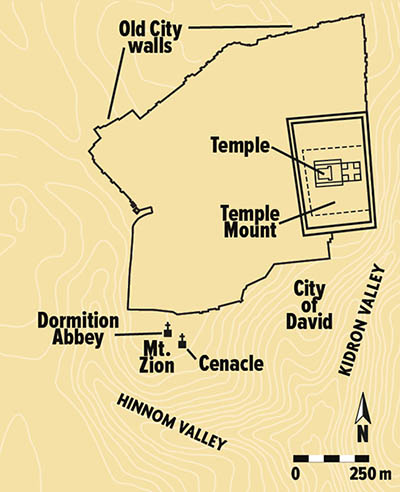

Jesus’ Last Supper and the Tomb of David are traditionally associated with the Cenacle on Mount Zion.
Regrettably, no archaeological excavation has ever been attempted at or around the alleged site of Jesus’ Last Supper and the Tomb of David on Mount Zion to assess the development, relationship or even age of the built structures. Only limited probing and non-invasive soundings were performed at different times in history—typically in association with new construction or renovation at the site.
Jerusalem lies at the heart of Biblical archaeology. In the free eBook Jerusalem Archaeology: Exposing the Biblical City, learn about the latest finds in the Biblical world’s most vibrant city.
In his latest book,2 Clausen looks at all the extant historical evidence and tries to make sense of what the limited archaeological data tell us when interpreted together with contemporary artistic representations, literary sources, accounts by Western pilgrims and the various traditions passed on through the ages.
In unraveling the complex story, Clausen tackles two sets of issues: First, when was the building we now call the Cenacle established, and what were its functions over the centuries? Second, where are the actual sites of Jesus’ Last Supper and the Tomb of David?
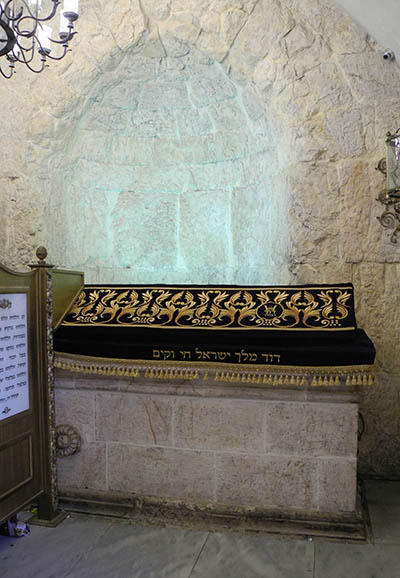


The presumptive Tomb of David is commemorated in the Cenacle on Mount Zion by this cenotaph. The niche visible behind the cenotaph is seen by some as evidence for the space having been a synagogue in antiquity. Photo: Courtesy of David C. Clausen.
Biblical texts locate the Tomb of David in the City of David, the ancient settlement overlooking the Kidron Valley (1 Kings 2:10 and Nehemiah 3:14–16). It was apparently only in the Middle Ages that the burial place of King David began to be expressly associated with Mount Zion. Adding to the puzzle, however, is the uncertain location of the Biblical Zion vs. the modern-day Mount Zion. Can we safely identify the Biblical Zion with the western hill we now call Mount Zion?
Modern scholars generally argue that the Biblical Zion was located on the hill east of the present-day Mount Zion, on the site where the formerly Jebusite City of David stood; they also mostly agree that Mount Zion came to be identified with the western hill only around the turn of the era. It is thus highly unlikely that the Cenacle has anything to do with the actual tomb of David.3
Where Jesus’ Last Supper took place as narrated in the Gospels is even more intricate. Unlike with the tomb of David, the location of the Last Supper’s cenacle is not specified in the Bible.4 Nor is the location of a number of other events associated with the same building clear, including appearances by the risen Jesus (Luke 24:36; John 20:19–29), the selection of Matthias the twelfth apostle (Acts 1:26), the first Pentecost following Easter Sunday (Acts 2:1–14), and the interment of Jesus’ brother James. And literary sources, such as the anonymous pilgrim from Bordeaux and Egeria who associate the location of Jesus’ Last Supper with Mount Zion, go back only to the fourth century C.E.
As the alleged place of congregation and worship for early Christians in Jerusalem, the Cenacle on Mount Zion would be the first Christian church ever.5 So, did subsequent churches at the site of today’s Cenacle honor the location of the original Upper Room? Was the Byzantine basilica of Hagia Sion (“Holy Zion”)—built in 379–381 C.E. and demolished in 1009 C.E.—constructed to incorporate the house where Jesus’ Last Supper happened? Called “the mother of all churches,” the Hagia Sion might have been, but the sixth-century mosaics of Jerusalem from Santa Maria Maggiore in Rome and St. George Church in Madaba, Jordan, which are the two earliest artistic representations of the basilica, do not support this opinion, but rather show an autonomous structure standing to the south of the Holy Zion Church.
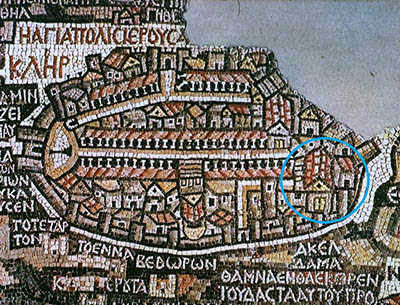

This sixth-century C.E. mosaic map of Jerusalem from the Church of St. George in Madaba, Jordan, shows the large Byzantine basilica on Mount Zion with a small building next to it (encircled), which might be the building traditionally identified as the “Upper Room” of Jesus’ Last Supper and the Tomb of David.
Next, what is the relationship of the earliest architectural stages of the Cenacle to the Crusader-period Church of Virgin Mary and to the modern Dormition Abbey and the Basilica of the Assumption (or Dormition), built in the early 1900s over the western end of the Byzantine-era Hagia Sion?


A mosaic in the Santa Maria Maggiore Church in Rome depicts a large basilica on Mount Zion flanked by a small building—the cenacle of Jesus’ Last Supper and the Tomb of David? Photo: Courtesy of David C. Clausen.
But, most fundamentally: Do the Cenacle’s origins actually date back to Jesus’ time? Without new hard evidence—such as from excavations—this is impossible to tell for sure. Did other Biblical events traditionally associated with this building really take place at the same spot? We might never know.


Re-used in this medieval, Islamic-period dome inside the Cenacle is a Crusader-era column capital with carved eagles and other Christian symbols. Photo: Courtesy of David C. Clausen.
Some scholars, including Amit Reem of the Israel Antiquities Authority, maintain that the structures detected under the Cenacle are nothing more than just remains of a late-fourth-century Byzantine church, the Holy Zion basilica. Clausen, however, asserts that the Cenacle’s oldest elements did originate before the Byzantine period.
To learn Clausen’s full argument, read his Archaeological Views column “Mount Zion’s Upper Room and Tomb of David” in the January/February 2017 issue of Biblical Archaeology Review.
——————
Subscribers: Read the full Archaeological Views column “Mount Zion’s Upper Room and Tomb of David” by David Christian Clausen in the January/February 2017 issue of Biblical Archaeology Review.
Not a subscriber yet? Join today.
Jerusalem lies at the heart of Biblical archaeology. In the free eBook Jerusalem Archaeology: Exposing the Biblical City, learn about the latest finds in the Biblical world’s most vibrant city.
Notes:
1. “Room upstairs” in the opening quote from Luke’s gospel corresponds in the original Greek text to the word anagaion, which denotes any upper-floor room (or elevated part) of the house. In Luke’s gospel, it serves as a dining-room (hence the Latin coenaculum).
2. David Christian Clausen, The Upper Room and Tomb of David: The History, Art and Archaeology of the Cenacle on Mount Zion (Jefferson, NC: McFarland, 2016).
3. See Jeffrey R. Zorn, “Is T1 David’s Tomb?” BAR, November/December 2012.
4. See Matthew 26:17–20; Mark 14:12–17; Luke 22:7–12.
5. See Bargil Pixner, “Church of the Apostles Found on Mt. Zion,” BAR, May/June 1990.
Related reading in Bible History Daily:
Was Jesus’ Last Supper a Seder? by Jonathan Klawans
Jesus’ Last Supper Still Wasn’t a Passover Seder Meal by Jonathan Klawans
The Last Days of Jesus: A Final “Messianic” Meal by James Tabor
Pilgrims’ Progress to Byzantine Jerusalem
This Bible History Daily feature was originally published on February 9, 2017.
Get more biblical Archaeology: Become a Member
The world of the Bible is knowable. We can learn about the society where the ancient Israelites, and later Jesus and the Apostles, lived through the modern discoveries that provide us clues.
Biblical Archaeology Review is the guide on that fascinating journey. Here is your ticket to join us as we discover more and more about the biblical world and its people.
Each issue of Biblical Archaeology Review features lavishly illustrated and easy-to-understand articles such as:
• Fascinating finds from the Hebrew Bible and New Testament periods
• The latest scholarship by the world’s greatest archaeologists and distinguished scholars
• Stunning color photographs, informative maps, and diagrams
• BAR’s unique departments such as First Person and Strata
• Reviews of the latest books on biblical archaeology
The BAS Digital Library includes:
• 45+ years of Biblical Archaeology Review
• 20+ years of Bible Review online, providing critical interpretations of biblical texts
• 8 years of Archaeology Odyssey online, exploring the ancient roots of the Western world in a scholarly and entertaining way,
• The New Encyclopedia of Archaeological Excavations in the Holy Land
• Video lectures from world-renowned experts.
• Full online access to 50+ curated Special Collections,
• Four highly acclaimed books, published in conjunction with the Smithsonian Institution: Aspects of Monotheism, Feminist Approaches to the Bible, The Rise of Ancient Israel and The Search for Jesus.
The All-Access membership pass is the way to get to know the Bible through biblical archaeology.

